Introduction
Picture this: You’re at your desk, sipping your morning coffee, when suddenly your screen goes dark. A menacing message appears, demanding a hefty ransom to unlock your precious business data. Your heart races as you realize your entire operation has ground to a halt. But wait – you’ve got backups, right? …Right?
In today’s digital Wild West, where cyber outlaws are constantly upping their game, your backups aren’t just a safety net – they’re your secret weapon. But here’s the kicker: even your backups need protection.
Join us as we dive into the nitty-gritty of backup security. Whether you’re a small business owner burning the midnight oil or an IT pro juggling a million tasks, this guide is your ticket to sleeping soundly at night. We’ll walk you through battle-tested strategies to keep your data safe from everything from crafty hackers to good old-fashioned “oops” moments.
Ready to turn your backups into an impenetrable fortress? Let’s dive in and make your data untouchable.
Why Is Protecting Backups Critical for Small Businesses?
Backups play a pivotal role in maintaining business continuity. However, just having a backup is not enough — protecting those backups is key to ensuring their availability when needed most.
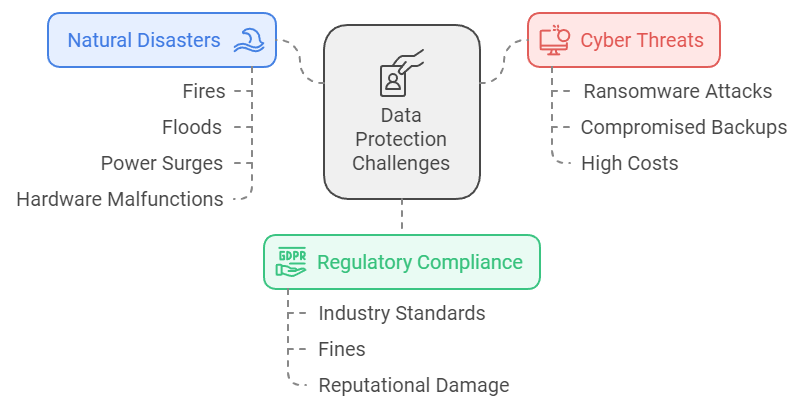
- Data Breaches and Cyber Threats: Ransomware attacks have become sophisticated, not only targeting primary data but also compromising backups to demand a ransom. The average cost of a data breach for small businesses can reach thousands of dollars, and unprotected backups may expose businesses to further data loss or unauthorized access.
- Natural Disasters and Hardware Failures: Fires, floods, power surges, or hardware malfunctions can cause irreversible data loss. Ensuring your backups are securely stored in different physical or cloud-based locations helps reduce these risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require businesses to follow stringent data protection standards. Failing to properly secure backups could result in fines or reputational damage.
By understanding these risks, businesses can better appreciate the need to implement robust backup protection strategies.
Types of Backups and Their Security Implications
Choosing the right type of backup strategy depends on your business needs and the level of protection required. Here’s a look at common backup types and their security implications.
Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
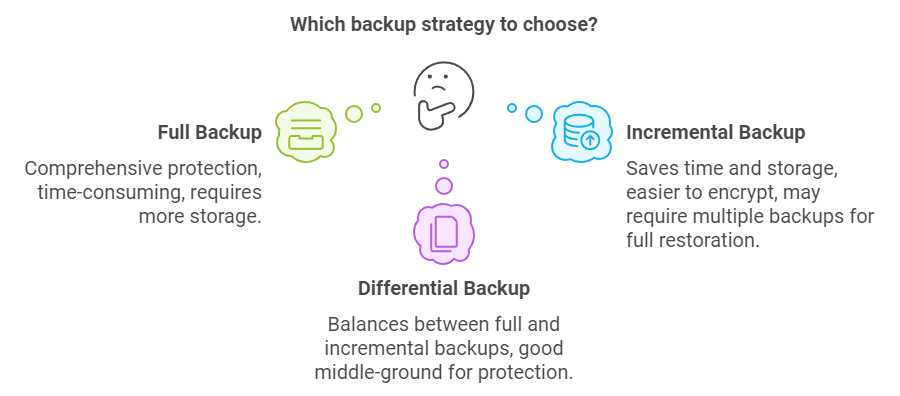
- Full Backups: A complete copy of all your data. It offers comprehensive data protection but can be time-consuming and require substantial storage.
- Security Implications: Since full backups contain all data, it’s crucial to encrypt them to prevent unauthorized access.
- Incremental Backups: Only backs up data that has changed since the last backup, saving time and storage space.
- Security Implications: Faster and easier to encrypt but may require a series of backups to restore data fully.
- Differential Backups: Backs up all changes made since the last full backup. It balances between full and incremental backups in terms of time and storage.
- Security Implications: A good middle-ground for protection; encryption is also vital for this backup type.
On-Site vs. Off-Site Backups
- On-Site Backups: These are stored locally on your premises, such as on external hard drives or local servers.
- Pros: Quick access and recovery.
- Cons: Susceptible to physical theft, damage, or disaster (fire, flood).
- Off-Site Backups: Stored away from your primary business location, either on remote servers or in the cloud.
- Pros: Protected from local disasters and often more secure with cloud providers offering encryption.
- Cons: Recovery may take longer due to remote access.
Table:
| Backup Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Complete data protection | Time-consuming, storage-heavy |
| Incremental Backup | Fast, storage-efficient | Longer restoration process |
| Differential Backup | Faster restore than incremental | More storage than incremental |
Best Practices for Securing Your Backups
To protect your business’s critical data, follow these best practices:
Encrypt Your Backups
Encryption is one of the most effective methods to secure your data backups. Encrypting data both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when being transferred) prevents unauthorized access.
- AES-256 Encryption: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256) is widely regarded as secure and is commonly used for encrypting backups.
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypts data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring no unauthorized parties can access it.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Backup Access
Implementing MFA ensures only authorized users can access backup systems. Even if a password is compromised, an additional verification step (e.g., text message code, app authentication) will help secure backup access.
Steps to Implement MFA:
- Enable MFA in your backup management software.
- Set up app-based authentication (e.g., Google Authenticator) or text-based codes.
- Regularly update MFA settings and educate users on proper authentication procedures.
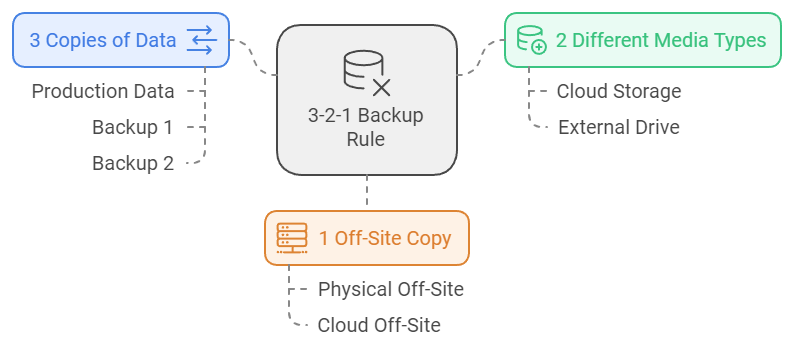
Use the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
A well-known rule for ensuring effective backup protection:
- 3 Copies of Your Data: Maintain three versions of your data (production data + two backups).
- 2 Different Media Types: Store your data on at least two types of storage media (e.g., cloud and external drive).
- 1 Off-Site Copy: Keep one copy off-site, either physically or in the cloud.
Regularly Test Backup Integrity and Recovery
Testing backups ensures that data can be restored effectively in case of data loss.
- How to Test: Periodically attempt a full restoration to verify that all files are intact.
- Frequency: Quarterly or bi-annually, depending on how critical the data is.
Protecting Backups from Ransomware and Cyber Threats
Implement Immutable Backups
Immutable backups are write-protected and cannot be altered once created. This feature helps prevent ransomware from modifying or deleting backup data.
- Setting Up Immutability: Use backup software that supports immutable storage or cloud providers offering immutable storage options.
Use Backup Solutions with Ransomware Detection
Modern backup solutions often include ransomware detection by scanning for unusual activities or changes in data patterns. Choose a solution that provides automated alerts and mitigates ransomware risks.
Recommended Solutions:
- Acronis: Offers AI-based ransomware protection and backup encryption.
- Veeam: Provides ransomware resilience features like immutable backups.
Regularly Update Backup Systems and Software
Outdated backup software is vulnerable to attacks. Regularly update and patch your backup systems to prevent exposure to known security vulnerabilities.
Choosing the Right Backup Solution for Your Business
On-Premises vs. Cloud Backup Solutions
When selecting a backup solution, consider your business needs:
- On-Premises: Offers control over your data but requires physical security and maintenance.
- Cloud Backup: Provides off-site storage, automated backups, and often includes enhanced security features like encryption and MFA.
Evaluating Backup Solutions: What to Look For
When choosing a backup solution, evaluate:
- Security Features: Encryption, MFA, ransomware detection.
- Scalability: Can it handle your growing data needs?
- Cost and ROI: Is the solution cost-effective, providing good value for the security it offers?
Comparison Table:
| Backup Solution | Security Features | Scalability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acronis | Ransomware protection | High | Affordable |
| Veeam | Immutable backups | Scalable | Moderate |
| Backblaze | Easy-to-use cloud backup | High | Low-cost |
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I back up my data?
It depends on your business needs, but generally, daily backups are recommended for critical data. For less critical data, weekly or monthly backups may suffice.
What is the safest way to store backup data off-site?
Cloud backups with strong encryption and access controls are typically the safest. Secure physical storage in a different location is also effective.
Can ransomware affect my backups?
Yes, ransomware can target backup data. That’s why it’s essential to have immutable backups and regularly test backup integrity.
Conclusion
Securing your backups is crucial for maintaining business continuity, protecting sensitive information, and ensuring quick recovery after any data loss event. By following best practices such as encryption, the 3-2-1 backup rule, and using ransomware-resistant solutions, small business owners and IT professionals can significantly enhance the protection of their backup data.

