Introduction
Did you know that cyberattacks on defense contractors have increased by over 50% in the last few years? With sensitive data at stake, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) introduced the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) to safeguard national security. But what is CMMC exactly, and how does it impact businesses working with the DoD? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of CMMC, its importance, and how organizations can achieve compliance.
What Is CMMC?
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a unified standard for implementing cybersecurity across the defense industrial base (DIB). Established by the DoD, CMMC aims to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI) from cyber threats.
CMMC* integrates various cybersecurity standards and best practices, consolidating them into a set of guidelines that contractors must follow to secure their systems and networks. The certification encompasses multiple maturity levels, each with specific processes and practices to enhance an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
Why Is CMMC Important?
Protecting National Security
Cyber threats pose a significant risk to national security, especially when they target defense contractors handling sensitive information. Implementing CMMC ensures that all contractors meet a baseline cybersecurity standard, reducing vulnerabilities across the supply chain.
Mandatory for DoD Contracts
Starting from 2020, CMMC compliance became a prerequisite for bidding on DoD contracts. Without the appropriate CMMC certification, organizations cannot participate in defense projects, making compliance essential for business continuity in the defense sector.
Enhancing Organizational Cybersecurity
Beyond contractual obligations, CMMC compliance helps organizations strengthen their cybersecurity frameworks, protecting them from data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
Understanding the CMMC Model
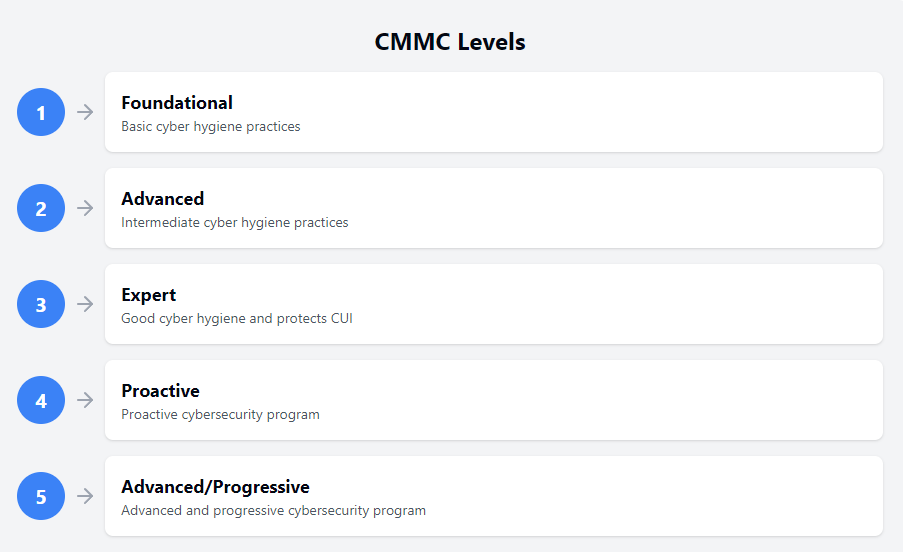
The Five Maturity Levels
CMMC is structured into five maturity levels, each representing the organization’s progression in cybersecurity practices:
- Level 1 – Basic Cyber Hygiene
- Implement basic safeguarding of FCI.
- Practices include antivirus usage and regular password updates.
- Level 2 – Intermediate Cyber Hygiene
- Serves as a transitional step towards protecting CUI.
- Incorporates select practices from NIST SP 800-171.
- Level 3 – Good Cyber Hygiene
- Focuses on protecting CUI.
- Requires adherence to all NIST SP 800-171 controls.
- Level 4 – Proactive
- Enhances protection against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
- Involves sophisticated cybersecurity measures.
- Level 5 – Advanced/Progressive
- Optimizes cybersecurity capabilities.
- Emphasizes the ability to repel APTs.
Domains and Practices
CMMC encompasses 17 domains, such as Access Control (AC), Incident Response (IR), and Risk Management (RM). Each domain contains specific practices and processes that organizations must implement to achieve the desired maturity level.
The CMMC Certification Process
Preparing for Certification
- Self-Assessment
- Evaluate current cybersecurity practices against CMMC requirements.
- Identify gaps and areas needing improvement.
- Develop an Action Plan
- Create a remediation plan to address deficiencies.
- Prioritize tasks based on risk and resources.
Engaging a CMMC Third-Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO)
- Select an Accredited C3PAO
- Only authorized organizations can conduct official CMMC assessments.
- Accredited C3PAOs on the CMMC Accreditation Body’s website
- Schedule the Assessment
- Coordinate timelines and resources.
- Undergo the Audit
- The C3PAO evaluates compliance with the required CMMC level.
- Receive Certification
- Upon successful assessment, receive certification valid for three years.
Implementing CMMC Practices
- Policy Development
- Document cybersecurity policies aligned with CMMC domains.
- Employee Training
- Educate staff on cybersecurity best practices and compliance requirements.
- Technology Solutions
- Deploy necessary tools, such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- Continuous Monitoring
- Regularly assess systems to ensure ongoing compliance.
Challenges in Implementing CMMC
Resource Constraints
- Small Businesses Impact
- Limited budgets may strain the ability to invest in required technologies and training.
- Solution:
- Seek government grants or collaborate with larger contractors for support.
Understanding Complex Requirements
- Technical Jargon and Standards
- Navigating NIST standards and CMMC specifics can be daunting.
- Solution:
- Hire cybersecurity consultants or attend CMMC training programs.
Official CMMC training providers
Keeping Up with Updates
- Evolving Standards
- CMMC guidelines may change, requiring organizations to adapt.
- Solution:
- Stay informed through official channels and adjust practices accordingly.
Benefits of Achieving CMMC Compliance
Competitive Advantage
- Preferred Contractors
- Being CMMC certified positions your organization as a reliable partner for the DoD.
- Market Differentiation
- Demonstrates commitment to cybersecurity, attracting potential clients.
Risk Mitigation
- Reduced Cyber Threats
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures lowers the risk of breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Avoid penalties associated with non-compliance.
Organizational Improvement
- Enhanced Processes
- Streamlining cybersecurity practices can improve overall operational efficiency.
- Employee Awareness
- Training programs foster a culture of security within the organization.
Conclusion
Understanding what CMMC is and implementing its requirements is no longer optional for defense contractors. Achieving CMMC compliance not only opens doors to lucrative DoD contracts but also fortifies your organization’s cybersecurity framework. By proactively engaging in the CMMC certification process, you position your business for long-term success in a competitive and security-conscious market.
Ready to embark on your CMMC journey? Start by conducting a self-assessment and developing a robust action plan today.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between CMMC and NIST SP 800-171?
While NIST SP 800-171 outlines the cybersecurity requirements for protecting CUI, CMMC incorporates these standards into a certification framework with additional processes and practices across five maturity levels.
2. Do all DoD contractors need to be CMMC certified?
Yes, all organizations within the DoD supply chain handling FCI or CUI must achieve the appropriate CMMC level to bid on contracts.
3. How long does it take to become CMMC compliant?
The timeline varies based on the organization’s current cybersecurity posture. It can take several months to a year to fully implement required practices and complete the CMMC certification process.
4. Can organizations self-certify for CMMC?
No, organizations must undergo an assessment by an accredited C3PAO to achieve official CMMC certification.
5. How often is CMMC certification renewed?
CMMC certifications are valid for three years. Organizations must be reassessed to maintain compliance.